DEFINITION OF GELS
Gels are transparent or translucent, non-greasy, semisolid systems preparation consisting of dispersions of small or large molecules in an aqueous liquid vehicle, which has been thickened with a gelling agent. Gels can be a single phase or a biphasic system.
Jels & Jellies both are semi-solid system dosage form but jellies have soften consistency than gels.
CLASSIFICATION OF GELS
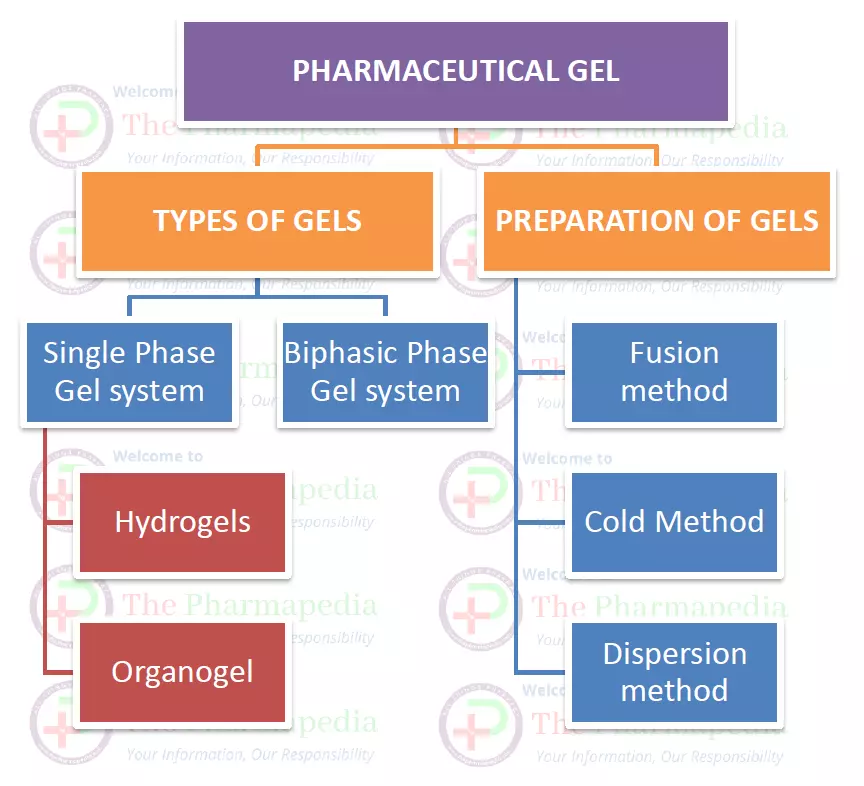
According to solubility of gelling agent into dispersion liquid, gels are classified into two classes.
A. One-Phase/monophasic gel system
- When the gelling agent is soluble in dispesing liquid, get single phase gel system.
- Example; Hydrophillic polymers (Hydrophillic pomymer is soluble in aqueous).
- Appearance: Clear
- Rheology- Pseudoplastic flow
- Single-phase gels use high molecular weight hydrophilic polymers as gelling agents. Examples of such polymers include carbomers (cross-linked acrylic acid polymers). These gels are considered to be one-phase systems because no definite boundaries exist between the dispersed macromolecules and the liquid.
- According to dispersing liquid medium, One-Phase gel system is further classified into following two class.
a) Hydrogels
b) Organogels
B. Biphasic/ two phase gel system
- Gelling agent is insoluble in dispersion liquid, we get biphasic gel system.
- Example: Aluminum hydroxide gel, Bentonite gel.
- Biphasic Gel system show Thixotropic flow behavior.
- Appearance- Turbid
- Biphasic gels could contain a gelatinous, cross-linked precipitate of one substance in the aqueous phase. For example, magma or milk of magnesia consists of a gelatinous precipitate of magnesium hydroxide.
Jellies are generally applied externally. They are used for medication, lubrication and some miscellaneous applications.
Jellies are used as lubricants for surgical gloves, catheters, and rectal thermometers. Lidocaine Hydrochloride Jelly is used as a topical anesthetic. Therapeutic vaginal jellies are available, and certain jelly-like preparations are used for contraceptive purposes, which often contain surface-active agents to enhance the spermatocidal properties of the jelly.
One base contains sodium alginate, glycerin, calcium gluconate, and water. The calcium ions cause a cross-linking with sodium alginate to form a gel of firmer consistency.
TYPES OF GELS
- 1. HYDROGELS
- 2. XEROGELS
- 3. ORGANOGELS
1. HYDROGELS
- A hydrogel is a network of polymer chains that are hydrophilic, sometimes found as a colloidal gel in which WATER/AQUEOUS is the dispersion medium.
- Hydrogels are highly absorbent(they can contain over 90% water) natural or synthetic polymeric networks.
- Hydrogels also possess a degree of flexibility very similar to natural tissue, due to their significant water content.
- Common ingredients include polyvinyl alcohol, sodium polyacrylate, acrylate polymers and copolymers with an abundance of hydrophilic groups.
Uses
- As scaffolds in tissue engineering.
- As environment sensitivity detector.
- Sustained release DDS.
- Contact lenses.
- ECG medical electrode.
- Glue
2. XEROGELS
Xerogels can be described as dried gels. Open network formed by the removal of all swelling agents from a gel. Xerogels usually retain high porosity (15–50%) and enormous surface area, along with very small pore size (1–10 nm). When solvent removal occurs under supercritical conditions, the network does not shrink and a highly porous, low-density material known as an aerogel is produced.
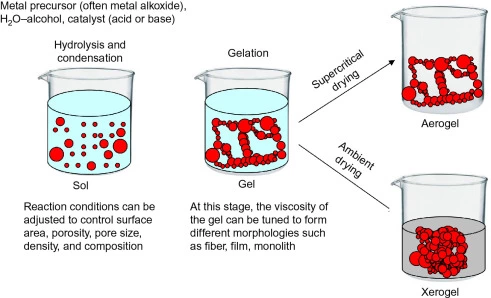
3. ORGANOGELS
An organogel is a non-crystalline, non-glassy thermo reversible (thermoplastic) solid material composed of a liquid organic phase entrapped in a three-dimensionally cross-linked network. The liquid can be, for example, an organic solvent, mineral oil, or vegetable oil. These systems are based on self-assembly of the structuring molecules.
CHARACTERISTIC OF GELS
- Jells have large proportion of water and water act as a vehicle for solubility of the drug.
- Gels are commonly used as topical preparations or used in body cavities.
- They are clear and turbid preparation depending upon solubility of ingredients.
- Gels may thicken upon long stand so gel should be shaken prior to use.
Methods of Preparation of Pharmaceutical Gels
Join WhatsApp channel to get latest Job notification, Study material, Previous paper, MCQ quiz, Admission alerts & News etc. for Pharmacy aspirants.
Subscribe our Telegram channel for Pharmacy Notes, MCQ Quiz, , Previous paper, Admission alerts & News etc. for Pharmacy professionals.
Join Telegram group for all Pharmacy books, Pharmacopoeia (IP, USP, BP), Pharmacy Notes, Previous Year Question papers in pdf format.










