To Prepare emulsion, there is a need for emulsifying agents and Formulation additives (Antioxidants, Preservatives, Humectants, Colors and flavorings agents).
An emulsion is prepared by shaking strongly the mixture of the two immiscible liquids or by passing the mixture through a mill known as the homogenizer. The emulsions thus prepared from the pure liquids are usually not stable and the two liquids separate out on standing. To get a stable emulsion, small quantities of certain other substances are added during preparation. The substances thus added to stabilize the emulsions are called emulsifiers or emulsifying agents. The substances commonly used as emulsifying agents are soaps of various kinds, long-chain sulphonic acids or lyophilic colloids like proteins, gum, and agar.
To Prepare emulsion, there is a need for emulsifying agents and Formulation additives (Antioxidants, Preservatives, Humectants, Colors and flavorings agents).
An emulsion is prepared by shaking strongly the mixture of the two immiscible liquids or by passing the mixture through a mill known as the homogenizer. The emulsions thus prepared from the pure liquids are usually not stable and the two liquids separate out on standing. To get a stable emulsion, small quantities of certain other substances are added during preparation. The substances thus added to stabilize the emulsions are called emulsifiers or emulsifying agents. The substances commonly used as emulsifying agents are soaps of various kinds, long-chain sulphonic acids or lyophilic colloids like proteins, gum, and agar.
Preparation of Emulsion
- Extemporaneous Methods
- Industrial/Large Scale Methods
1. Extemporaneous Methods
An emulsion is prepared by the following methods
- Dry gum method
- Wet gum method
- Bottle method (used for volatile oils)
2. Industrial/Large Scale Methods
- Industrial method:–
- Homogenizer
- Colloidal mill
- Ultrasonic
| Type of oil | Oil:Water:Gum ratio |
|---|---|
| Fixed oil | 4:2:1 |
| Mineral oils | 3:2:1 |
| Volatile oil | 2:2:1 |
Stability of Emulsion
- Dispersed droplets tend to fuse themselves and finally separated into two layers ( Since Cohesive force is greater than adhesive force).
- Cohesive force:- attractive force between the same type of molecules in liquids
- adhesive force:– force between unlike molecules
- If Cohesive force is more ⇒Coalescence of droplets ⇒ Separation of Phase. So Emulsifiers are used to prevent Coalescence/ regrouping of globules.
Emulsifying agent & Bankroft’s Rule
- Emulsions are the thermodynamically unstable system. The stability of the emulsion system can be increased by using an appropriate emulsifying agent.
- Emulsifying agent Stabilizes emulsion by preventing/Reducing the coalescence of dispersed globules.
- They act as Bridge between the polar and nonpolar phases and decrease the interfacial tension. ( emulsifying agent are amphiphilic in nature, have polar & nonpolar group).Emulsifier should have a balance between its hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups, produce a stable emulsion, be stable itself, be chemically inert, be non-toxic and cause no irritation on the application, be odorless, tasteless & colorless and be expensive.
- Emulsifying agents are classified into the following three groups.
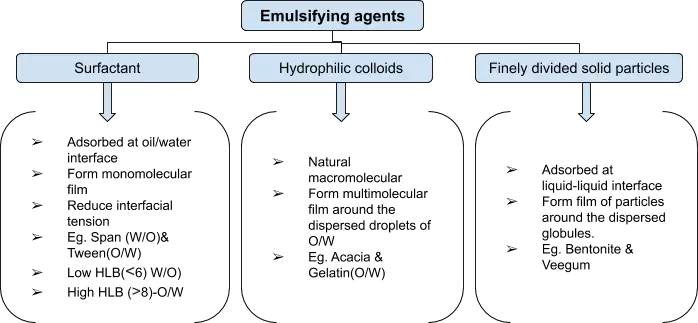
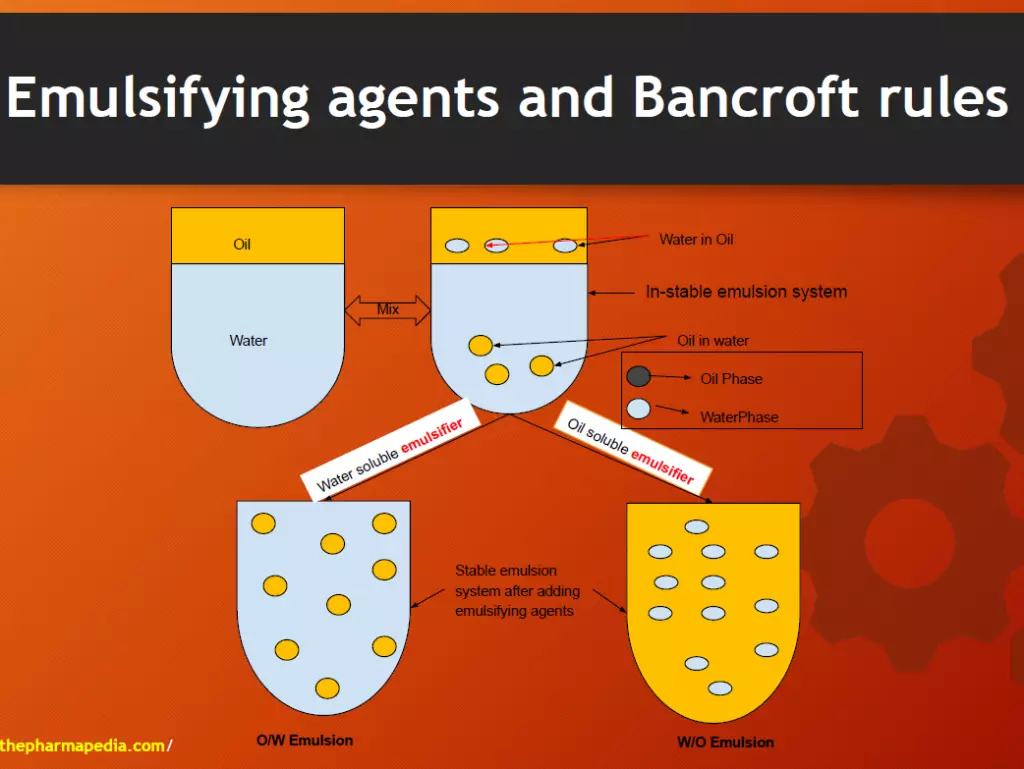
Bankroft’s Rule
- Describe the relationship between the nature of the emulsifying agent and type of emulsion formed.
- If a surfactant/emulsifying agent is more soluble in water, then the aqueous phase becomes continuous phase ⇒ O/W emulsion ⇒ eg. Tween, acacia, bentonite
- If oil-soluble emulsifier⇒ Nonaqueous phase becomes continuous phase ⇒ W/O emulsion ⇒ eg. Span
HLB (Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance for surfactant)
- Established by Griffin; Provide a scale of surfactant hydrophilicity; An emulsifier is a molecule with ambiphilic properties; Value range from 0 to 20.
- The relative solubility of the emulsifying agent in one of the phase is expressed by HLB scale.
- Emulsifier with high HLB value (8 to 16) ⇒ favor O/W emulsion
- Emulsifier with love HLB value (3-8) ⇒favor W/O emulsion
Also Read…
Introduction to Emulsion
Type of Emulsion
Identification of Emulsion
Physical Instability of Emulsion
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….










