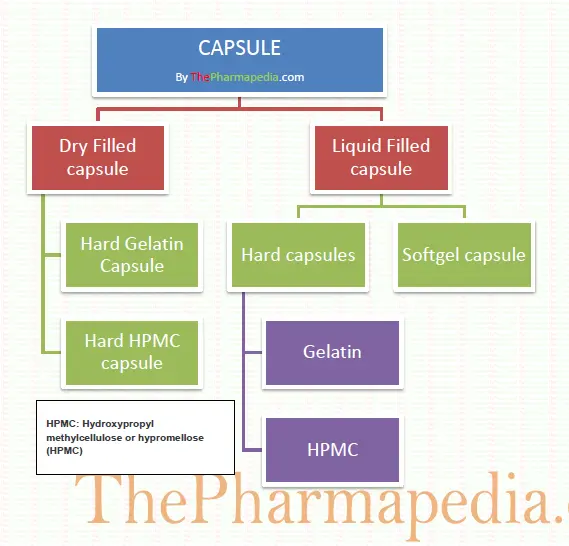
Depending on the nature of the capsule shell., Capsules may be classified mainly as either hard or soft. Other types of capsules are Modified release & Enteric Capsules.
- Hard Gelatin Capsule
- Soft Gelatin Capsule
- Modified Release Capsule
- Enteric Capsule
Types of Capsules

Also Capsule can be classified on following basis
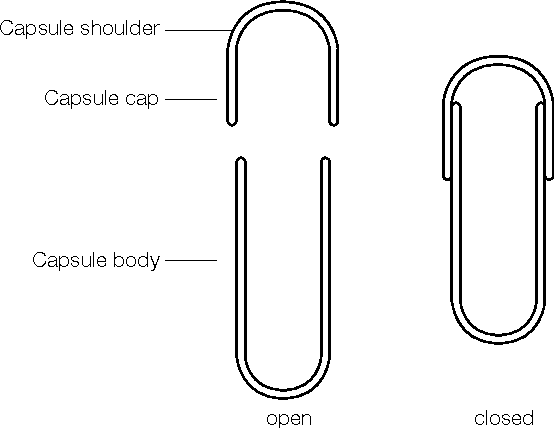
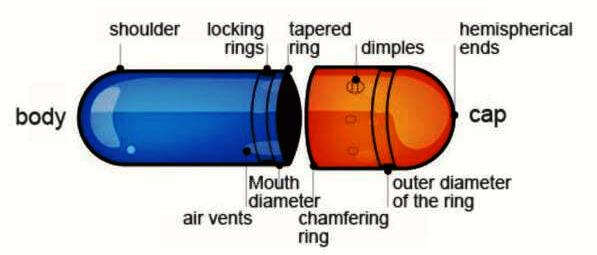
1. Hard gelatin capsules
Hard gelatin capsule is composed of two pieces (cap & body) in the form of cylinders closed at one end; the shorter piece called the ‘cap’ and the longer piece, called the ‘body,. Cap cover body part of capsule & body holds drug substance.
Size of Capsule
The two-piece hard gelatin capsule (for human use) is available in a range of sizes; from largest to smallest, these sizes are 000, 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
| Size of capsule | Volume (mL) | weight (m=V d (in gm)) |
|---|---|---|
| 000 | 1.37 | |
| 00 | 0.95 | |
| 0 | 0.68 | |
| 1 | 0.50 | |
| 2 | 0.37 | |
| 3 | 0.30 | |
| 4 | 0.21 | |
| 5 | 0.13 |
Note:
The approximate capacity for capsules from 000 to 5 ranges from 600 to 30 mg, depending on the densities of the powdered drug materials
Manufacturing of Hard Gelatin Capsule
Hard gelatin capsule are manufactured in one operation & filled in a completely separate operation.
Hard gelatin capsule mainly composed of gelatin and purified water. Some colored hard gelatin capsules also contain a small amount of Titanium dioxide and colorants.
| Name | Gelatin | Water | Titanium dioxide | Colorant |
| Transparent | 85% | 15% | / | / |
| Opaque | 83-84% | 15% | 0.5-1.8% | 0.2-0.5% |
I. Shell composition of Hard Gelatin Capsule
| Ingredient | Uses |
|---|---|
| Gelatin | often used a combination of pork skin & bone gelatin to get desired property of the gelatin shell |
| Colorant | Dye, pigments & (Iron oxides)- commonly used (Iron < 15ppm) |
| Opaquing Agents | TiO2 (titanium dioxide)- use to render shell opaque & to provide protection against light or to conceal the contents of the capsule |
| Preservatives | methyl-paraben & propyl-paraben & SO2 (Sulphur dioxide)– to prevent decomposition during manufacturing |
| Water | Purified water De-ionised water used to prepare gelatin solution for the preparation of dipping solution. |
| Plasticizers | Glycerin USP, Sorbitol USP (more common for soft gelatin capsules) |
II. Shell manufacturing
Automatic machines are used for hard capsule production consists of mechanisms for automatically dipping, spinning, drying, stripping, trimming, and joining the capsules.
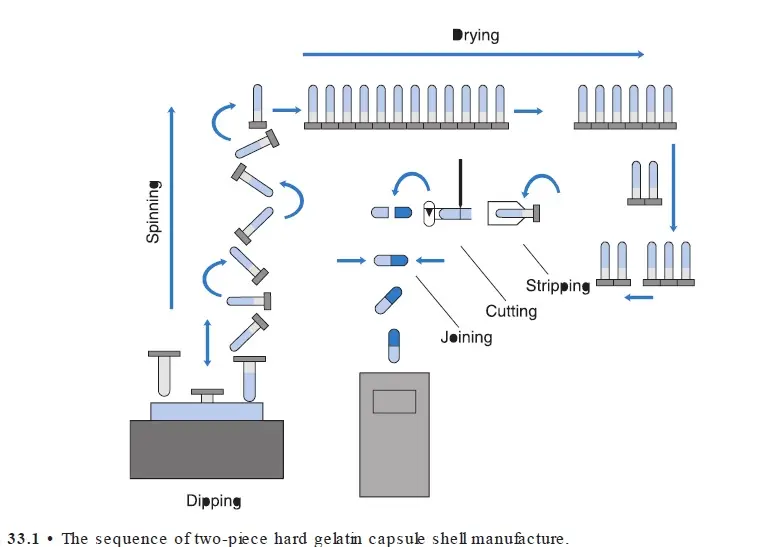
Steps involved in Hard Gelatin capsule Manufacturing
1. Dipping:
One hundred and fifty pairs of these pins are dipped, into a gelatin sol (about 12 seconds)of controlled viscosity at 50 oC temp. to form caps and bodies simultaneously.
2. Spinning/rotation
The pins are usually rotated to distribute the gelatin uniformly.
3. Drying
The pins are moved through a controlled air drying & precisely controlled removal of water
4. Stripping
The capsules are stripped from the pins by bronze jaws and
5. Trimming
Stripped Capsules are trimmed to length by stationary knives.
6. Joining
After being trimmed to exact length, the cap and body sections are joined and ejected from the machine.
Note: Thickness of the capsule wall is controlled by the viscosity of the gelatin solution and the speed and time of dipping.
III. Moisture Content
- Moisture can diffuse through the gelatin wall/film.
- Finished Hard gelatin capsules – optimum 13-16% moisture content (12-15% Lackman)
- If Moisture content less than< 12% – shell become brittle and suffer dimensional changes.
- If Moisture content of Shell more than 18% – shell become too soft & Result in a loss of mechanical strength.
- size variation in empty capsules aa result of moisture content variation.
IV. Storage of Empty Hard Gelatin Capsule
- Should storage at – 40-60% RH/relative humidity & Temp= 100 oF
Types of dosage forms for filling into hard capsules
| Solid | Semi-solid | Liquid |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Pellets Granules Tablets Capsules | Pastes Thermosofting mixture Thixotropic mixture | Non aqueous solutions Oil liquids |
Powder filling in the hard gelatin capsule
- Loading of empty capsule shell in filling machine
- Rectification of the capsule shell
- Separation of the body & cap.
- Filling the body with formulation
- Joining of the body & cap
- Ejection of the filled capsule
- Finishing – Dusting & Polishing –
- Pan polishing
- Cloth dusting
- Brushing
Soft Gelatin Capsule:
The soft gelatin capsule (SGC) was invented by Mothes, a French pharmacist, in 1833. It is One piece, hermetically sealed of gelatin shell containing, liquid, a suspension or a semisolid.
The composition of soft gelatin capsules is similar to that of hard gelatin capsules, except that the different moisture proportion & Plasticizers. Usually, plasticizers will be added to keep capsules’ elasticity and stability, including Glycerol, Sorbitol etc. It may contain preservative to prevent the fungal growth.
HPMC capsules
HPMC Capsule is mainly composed of HPMC and purified water. HPMC is a kind of cellulose obtained by the hydrolysis of plants and is made by etherification.
HPMC capsules are stable at low humidity levels, have low moisture content (3–8%), and low static charge. These natural HPMC capsules are suitable for highly reactive molecules (because they have no cross-linking reactions). Compared to hard gelatin, HPMC is more suitable for moisture-sensitive products, hygroscopic products, and for low relative-humidity applications.
Because HPMC is derived from plants, it is a vegetarian capsule (herbal product).
Modified Release Capsule
Both hard or soft gel capsules can be chemically modified to alter the release of the active ingredient(s). If the drug is water-soluble and in a hard capsule and a fast release is desired, the excipients should be hydrophilic and neutral whereas for slow release of water soluble drugs the excipients will slow the release. Rapid release from capsules can also be obtained by piercing the outer film with small holes or incorporating a small quantity of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate to assist in opening the capsule by evolution of carbon dioxide.
A small concentration (up to 1%) of sodium lauryl sulfate may be added to the gel of a soft capsule to enhance penetration of water and speed dissolution. If slow release from a soft capsule is required, polymer or alginates may be added.
Enteric Coated Capsules
Enteric Coated Capsules do not belong to a certain type of capsules. They are made by applying an enteric coating to other common capsules. Enteric Coated Capsules are mainly made to meet the needs of releasing medication in the intestine.
Its general principle works like that, with the coating process, the enteric capsule only can be dissolved by the alkaline liquid in the intestinal tract.
Starch capsules
Starch capsules are made from potato starch. Their dissolution is pH independent, and they are suitable for enteric coating. The moisture content of starch capsules ranges between 12–14% w/w, with more than 30% being tightly bound.
Pullulan capsules
These vegetarian capsules are made from tapioca, which is naturally fermented into pullulan. They provide a high barrier to oxygen.
Pullulan is a water-soluble mucopolysaccharide, a mature food additive
Polyvinl acetate (PVA) capsules
Capsules made from PVA can be used for filling insoluble drugs dissolved in polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400. PEG 400 when used as single vehicle is not compatible with other hard capsules. The oxygen permeability of PVA is low, resulting in a high barrier to oxygen.
Liquid-filled hard capsules
Two-piece hard capsules made of either gelatin or HPMC can be used for filling and band sealing non-aqueous liquid, paste, suspension, hot melts, and other vehicles that melt up to 70 °C and flow easily. LFHC can also be filled with tablets, pellets, or other capsules as combination fill. LFHC can be used for moisture-sensitive drugs. These can be a cost-effective alternative to some soft gelatin capsule products and can also enhance bioavailability and improve product stability. Liquid encapsulation technology helps overcome many problems associated with the use of softgel capsules including high cost, waste, cross-contamination, migration of the drug into the capsule shell, and issues with low bioavailability. Liquid-filled and semi-solid capsules by their nature are resistant to crushing and powdering and therefore provide a good basis for developing an abuse-resistant formulation. These capsules can also be enteric coated. HPMC hard capsules do not become brittle when they lose water.
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….










