Staining techniques in Microbiology
Under light microscope, structural detail of bacteria cannot see due to lake of contrast. To produce Colour contrast, staining methods are used to stain fixed smear of bacterial culture.
Smear is prepared from bacterial culture or specimen by drying and then fixed with heat by flaming the slide from underneath. Heat kills and fixes the bacteria on the slide due to a coagulation of bacterial protein.
| S. NO. | Staining technique | Dye | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Simple Staining | Methylene blue/ basic Fuchsin | Impart same colors to all bacteria |
| 2. | Negative Staining | India Ink/ Nigrosin | Demonstration of bacterail capsules |
| 3. | Impregnation method | Siver | Demonstration of bacterial flagella & Spirochaetes |
| 4. | Differential Staining | ||
| a. Gram staining | primary stain: crystal violet; Gram’s iodine (mordant); decolorizing agent (ethanol/ acetone); Secondary counterstain:safranin | To find out gram-positive bacteria (resist decolorization & retain the color of primary stain i.ee violet)& gram-negative bacteria (decolorized by acetone/ethanol & therefore take counterstain i.e. safranin & appear Red) | |
| b. Acid fast staining | Carbol fuchsin; 20 % Sulphuric acid (decolorization); Counterstain-methylene blue | Staining of Mycobacteria (tubercle & lepra bacilli); acid fastness is due to high lipid content Mycolic acid | |
| c. Alberts stains | Albert II iodine solution | Staining of Corynebacteria diphtheriae |
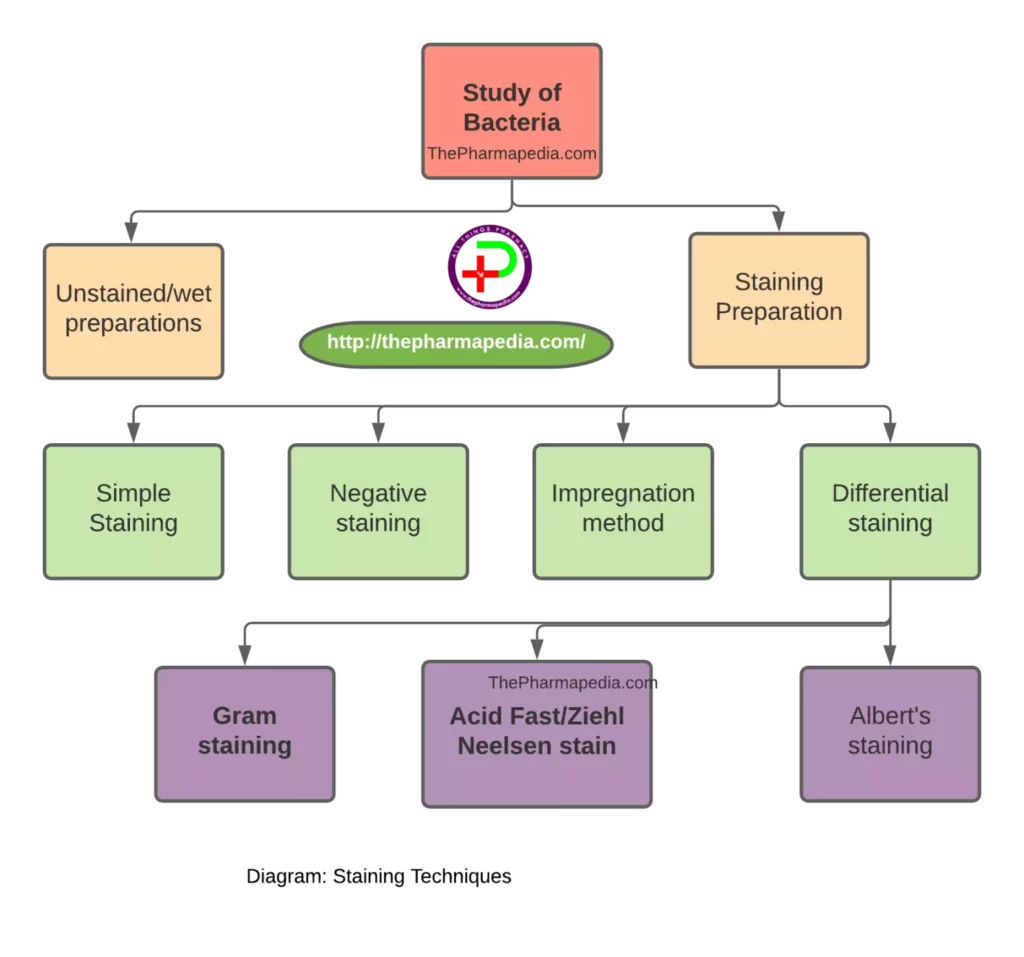
Following various staining techniques are used for the study of bacteria.
A. Unstained/wet preparation
These preparations are used to study bacterial motility (Example hanging drop preparation) & for demonstration of spirochaetes ( dark ground microscopy).
B. Staining preparations for bacteria
Due to lack of contrast, the structure of bacteria cannot be seen under a microscope. Hence to produce Colour contrast, staining methods were developed.
In the staining technique, bacterial culture is fixed on the slide with heat by flaming underneath slide. Fixed smear is stained by various following staining technique.
1. Simple staining,
2. Negative staining
3. Impregnation method
4. Differential staining
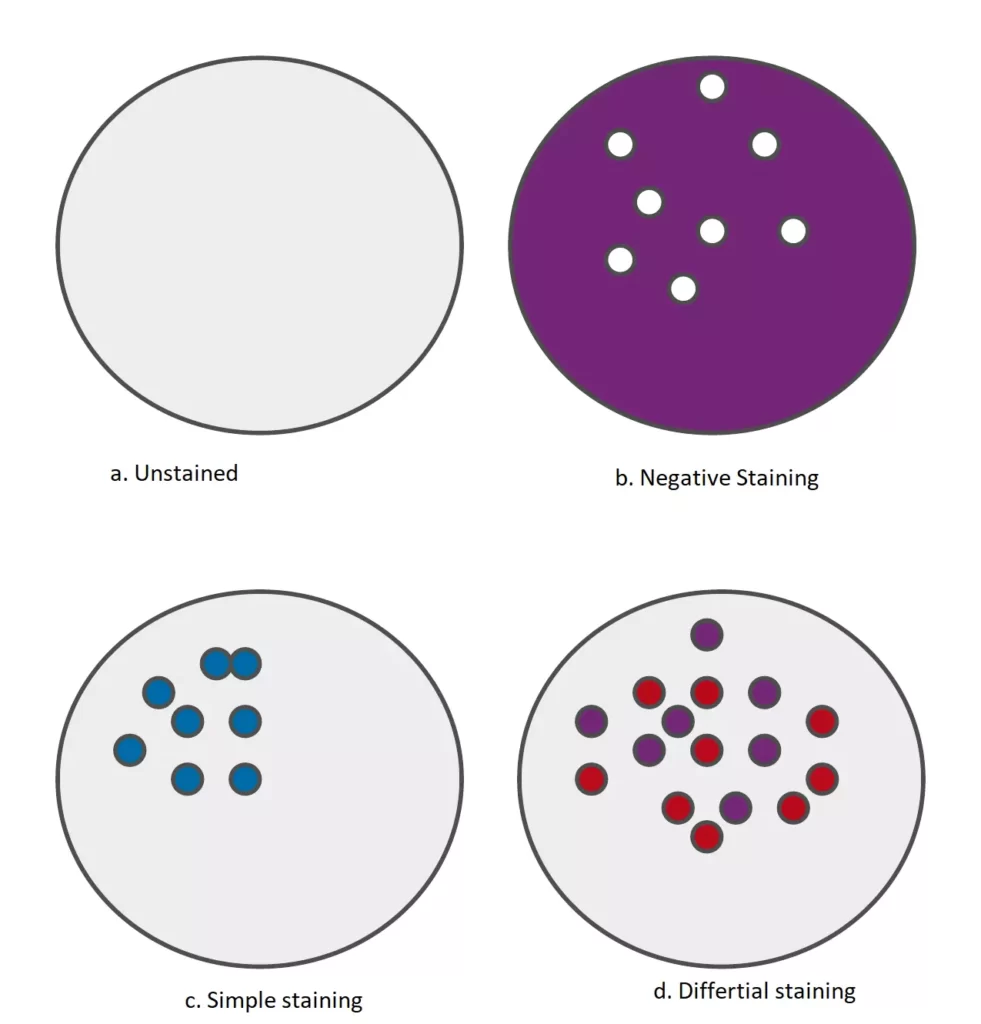
1. Simple staining
Simple stain imparts same colour to all the bacteria in smear
Example with Thailand blue and basic fuchsin dye.
Advantage of Simple Staining
- Simple staining is a reasonably simple procedure that just requires one reagent to stain the organism.
- It is a quick technique that takes only 3-5 minutes to complete the performance.
- Simple staining helps in examining or elucidating the shape, size, and arrangement of the microorganisms.
- It also enables us to distinguish between bacterial cells and inanimate objects.
- Simple staining might be helpful in the preliminary analysis of the morphological characters of the bacteria.
2. Negative staining
In this technique, background gets stained and unstained bacteria stand out in contrast under microscope.
Example: negative staining is used to demonstrate bacterial capsule (since capsule do not take stain)
3. Impregnation method
The very thin structure of bacteria is thickened by the impregnation of silver to make them visible under a microscope. Example demonstration of bacterial flagella and spirochaetes.
4. Differential staining
As name indicates these technique imparts different colour to different bacteria or bacterial structure. Differential stain technique includes the following technique
a. Gram staining read more...
b. Acid fast/Ziehl -Nelson staining read more…
c. Albert’s staining read more…