Monophasic liquid dosage form (MLDF) are the liquid preparation containing two or more component (solute) in one phase system.
Monophasic liquid dosage form (MLDF) is represent by true solution.
True solution:- It is a clear homogenous (one phase) mixture that is prepared by dissolving a solid, liquid or gas in liquid, represent an one phase so also termed as the monophasic liquid dosage form.
Solutions
A solution is a homogeneous mixture that is prepared by dissolving a solid, liquid, or gas in another liquid and represents a group of preparations in which the molecules of the solute or dissolved substance are dispersed into the solvent. or Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of one or more solutes molecularly dispersed in a suitable solvent or a mixture of mutually miscible solvents. The components of solutions are termed the solute and the solvent depending on their relative proportions (a component in lower proportion is termed solute).
Most solutions are unsaturated with the solute. The strengths of pharmaceutical solutions are expressed in terms of percentage strength, although for very dilute preparations expressions of ratio strength are sometimes used.
w/v, v/v, or w/w means percentage weight-in-volume for solutions or suspensions of solids in liquids; percentage weight-in-volume for solutions of gases in liquids; percentage volume-in-volume for solutions of liquids in liquids; and weight in-weight for mixtures of solids and semisolids pharmaceutical.
Saturated solutions are solutions that, at a given temperature and pressure, contain the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in the solvent.
Isotonic solutions have similar tonicity as biological fluids. These solutions cause no swelling or contraction of the tissues with which they come in contact and produce no discomfort when instilled in the eye, nasal tract, blood, or other body tissues. Isotonic sodium chloride is a 0.9% w/v concentration of NaCl in water and is also called normal saline. A 5% w/w dextrose, also known as glucose, solution in water is also isotonic.
Pharmaceutical solutions are used for many routes of administration, including oral, rectal, vaginal, ophthalmic, parenteral, and otic. The most common solution dosage form is the oral liquid.
Pharmaceutical solutions may be classified as an oral solution, otic solution, ophthalmic solution or topical solution.
Types/Classification of Monophasic Liquid Dosage form
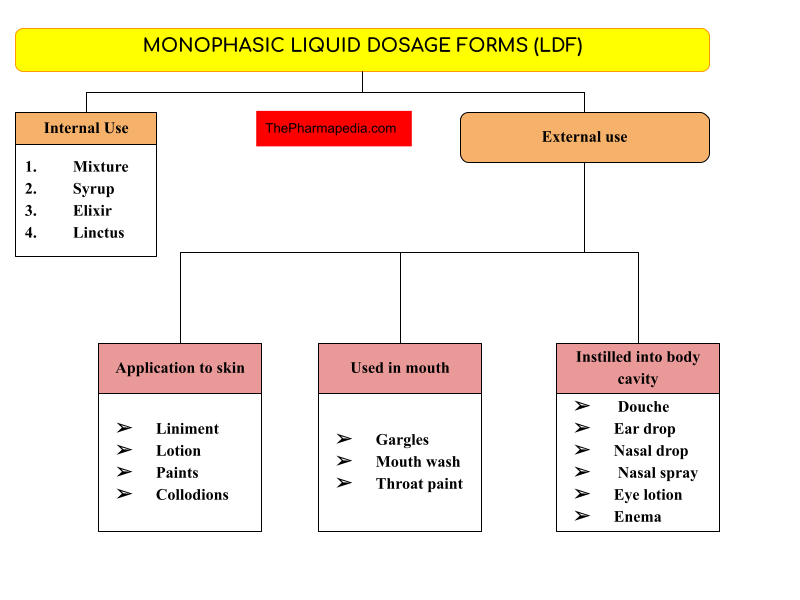
A. Solutions used for Internal Use/taken by an oral route
Click on the respective topic to read more…
Syrup
Mixture
Elixir
Linctus
B. Solutions used for External Use
Click on the respective topic to read more…
Solution application to Skin
Liniment
Lotion
Collodion
Solution used into Mouth
Click on the respective topic to read more…
Gargles
Mouth Wash
Throat Paint
Solution instilled into body cavities
Click on the respective topic to read more…
Ear Drop
Nasal Drop
Nasal Spray
Douche
Enemas
Solvents for Liquid Pharmaceutical Dosage Preparations
The selection of the appropriate solvent for a particular formulation depends upon on physical and chemical characteristics of a given drug. The active ingredient(s) may be dissolved in aqueous media, an organic solvent, or a combination of the two, by suspending the drug (if it is insoluble) in an appropriate medium or by incorporating the active pharmaceutical ingredient into one of the phases of an oil and water emulsion. Most commonly used solvents for Liquid dosage form are:-
- Water
- Alcohols
- Other-Glycerin, Propylene glycol
In most cases, especially solutions for oral, ophthalmic, or parenteral administration, water is the preferred solvent.
For Ophthalmic and parenteral preparation, the Preferred solvent is WFI (Water for Injection)
Purified water is used as a solvent for all preparation except Ophthalmic/parenteral & irrigations, or inhalations preparation.
Purified Water must be used for all other pharmaceutical operations, dosage forms, and, as needed, in all USP/IP tests and assays (Except preparation of parenteral, irrigations, or inhalations)
Types of Pharmaceutical water: Purified water, WFI, SWFI, BWFI, & BET click here
Other auxiliary solvents (Alcohol, glycerin, and propylene glycol) are also employed to increase the solvent action of water or to contribute to a product’s chemical or physical stability. Solvents, such as acetone and isopropyl alcohol, are too toxic for use in oral pharmaceutical preparations
Water
Water is used both as a vehicle and as a solvent for the desired flavoring or medicinal ingredients. Its tastelessness,
freedom from irritating qualities and lack of pharmacological activity makes it ideal for such purposes. Purified Water is obtained by deionization, distillation, ion exchange, reverse osmosis, filtration, or other suitable procedures.
Purified Water must be used for all other pharmaceutical operations, dosage forms, and, as needed, in all USP/IP tests and assays (Except preparation of parenteral, irrigations, or inhalations).
Note:
For parenteral administration, Water for Injection, Bacteriostatic Water for Injection, or Sterile Water for Injection must be used.
Alcohol
- Alcohol is the most commonly used solvent in pharmaceutical preparation after water for many organic compounds.
- When mixed with water, a hydroalcoholic mixture is formed capable of dissolving both alcohol-soluble and water-soluble substances,. This hydroalcoholic mixture is very useful for the extraction and purification of active constituents from crude drugs and synthetic procedures.
- Alcohol is a volatile solvent.
Alcohol USP: is 94.9–96.0% by volume, at 15.56°C of C2H5OH,
Dehydrated Alcohol USP:- contains not less than 99.5% C2H5OH by volume.
- Dehydrated alcohol is utilized when an essentially water-free alcohol is necessary.
- Due to pharmacologic and potential toxic effects of alcohol, concentration of alcohol in the oral liquid drug products of over-the-counter (OTC) has prescribed as:
- For the oral liquid drug products of OTC the recommended alcohol content limit
- oral products intended for children under 6 years of age, the recommended alcohol content limit is 0.5%;
- for products intended for children 6–12 years of age, the recommended limit is 5%; and
- for products recommended for children older than 12 years of age and for adults, the recommended limit is 10%.
Glycerin
It is a clear, syrupy liquid with a sweet taste and is miscible with water and alcohol. Glycerin is used in pharmaceutical formulations, including oral, otic, ophthalmic, topical, and parenteral preparations.
- Glycerin is used primarily for its humectant and emollient properties in topical pharmaceutical formulations and cosmetics.
- In parenteral formulations, glycerin is used mainly as a solvent.
- In oral solutions, glycerin is used as a solvent, sweetening agent, antimicrobial preservative, and viscosity increasing agent.
Propylene glycol
- Propylene glycol has become widely used as a solvent, extractant, and preservative in a variety of liquid pharmaceutical formulations, including parenteral.
- Propylene glycol is a viscous liquid and is miscible with water and alcohol. It is often used in place of glycerin.
- As an antiseptic, it is similar to ethanol, and against molds it is similar to glycerin and only slightly less effective than ethanol.
- It is non-volatile while alcohol is volatile
Preservative Used in Liquid Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and their Concentration
In general, drug substances are less stable in aqueous media than solid dosage forms. So that It is important to properly stabilize and preserve solutions/liquid from microbial/mold & oxidation.
- Preservatives (protected against microbial contamination/growth)
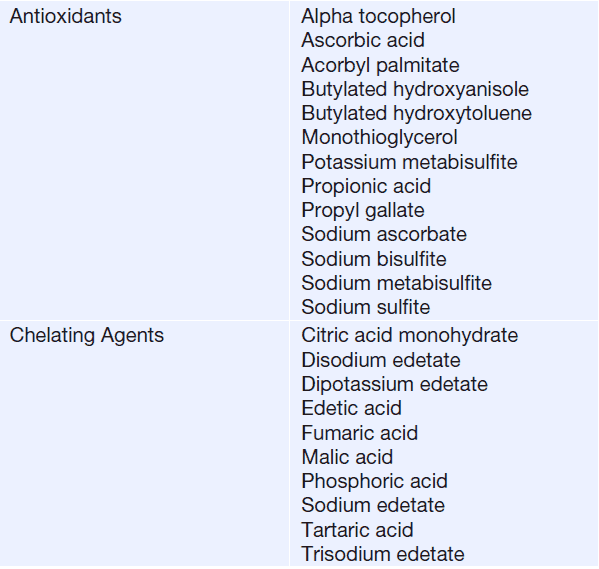
- Antioxidants and Chelating Agents (to stabilization of pharmaceutical preparations against chemical and physical degradation)
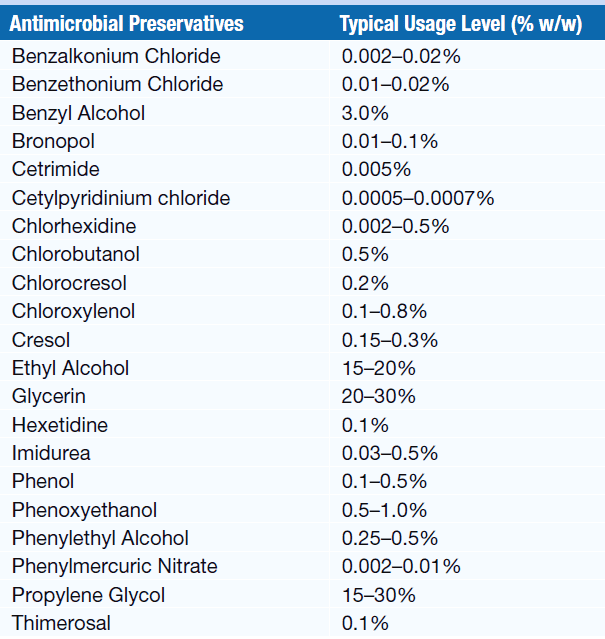
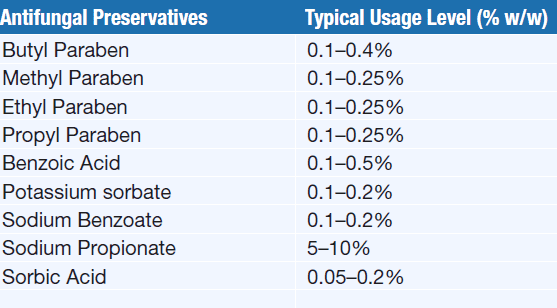
Preservatives Used in Liquid Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Their Concentration
Aqueous solutions, syrups, emulsions, and suspensions often provide excellent growth media for micro-organisms, such as molds, yeast, and bacteria & such preparation requires the presence of an antimicrobial preservative to maintain aseptic conditions throughout their stated shelf life.
The alcohol content of 15% by weight in acid solutions and 18% by weight in alkaline solutions is sufficient to prevent microbial growth. (elixirs, spirits, and tinctures, are self-preserving since these preparation contain alcohol).
Acidic preservatives (benzoic acid, boric acid, and sorbic acid, are less dissociated and more effective in acidic formulations. Similarly, alkaline preservatives are less effective in acidic or neutral conditions and more effective in alkaline formulations.
Antioxidant Used in Liquid Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
Vitamins, essential oils, and almost all fats and oils can be oxidized. Oxidation reactions can be initiated by heat, light, including ultraviolet radiant energy, peroxides, or other labile compounds or heavy metals, such as copper or iron.
Antioxidants may retard or delay oxidation by rapidly reacting with free radicals as they are formed quenching.
Collodions
Collodions are liquid preparations & they are applied to the skin by means of a soft brush or other suitable applicator and, when the ether and ethanol have evaporated, leave a thin film on the surface of skin. Collodions are liquid preparations containing pyroxylin, partially nitrated cellulose, in a mixture of ethyl ether and ethanol.
Salicylic Acid Collodion, USP, contains 10% w/v of salicylic acid in Flexible Collodion, USP, and is used as a keratolytic agent in the treatment of corns and warts.
Douches
- A douche is an aqueous solution used for rinsing or irrigate body cavities (sterile) for cleaning or removing foreign particles or discharges from them.
- It functions as a cleansing or antiseptic agent.
- An eye douche used to remove foreign particles and discharges from the eyes, Pharyngeal douches are used to prepare the interior of the throat for an operation and cleanse it in suppurative conditions. Similarly, there are nasal douches and vaginal douches are used to clean the nasal and vagina.
- Douches are administered by using bulb syringes.
- Douches are dispensed in the form of powder or tablet form with direction for dissolving it in a specific volume of warm water. Sometimes douches are supplied as s concentrated solution with direction to dilute is with a specific quantity of warm water before use.
- Douches are generally used for the following purposes:-
- Cleansing agents (Isotonic NaCl solution) – Sterile
- Antiseptic (HgCl2 0.001%, KMnO4 0.025%, Lactic acid 0.5 – 2%, Chlorhexidine 0.02%)
- Astringent (1% Alum)
Enemas
- Enemas are administered rectally for the local effects or systemic absorption. Rectal route of administration minimizes the undesirable gastrointestinal reactions associated with oral therapy.
- Enema preparations are rectal injection administered/employed to influence the general system by absorption, or to affect a local disease (retention enemas). Retention enemas are to be retained in the intestine and should not be used in quantities larger than 150 mL for an adult.
- A number of solutions are administered rectally for the local effects of the medication (e.g., hydrocortisone) or for systemic absorption (e.g., aminophylline).
- Sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, sodium monohydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, glycerin, docusate potassium and light mineral oil are used in enemas to evacuate the bowel (evacuation enemas).
Join Our WhatsApp Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to receive the latest updates like Pharma Job notifications, study materials, admission alerts, Pharma News, etc
Join Our Telegram Group to Download Free Books & Notes, Previous papers for D.Pharm, B.Pharm, M.Pharm, Drug Inspector & GPAT……….










