Definition
Capsule is solid dosage form in which the drug substance is enclosed in either a hard or soft, soluble container or shell of gelatin or other suitable material (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose). or
The capsule is a preparation in which drug substance(s) and/or excipients are enclosed in either a soft or hard soluble gelatin shell.
Traditional capsules are made from gelatin, which is a widely produced animal-based gelatin product. More recently HPMC (hydroxyprolymethyl cellulose) and Pullulan have become successful alternatives and are available commercially for both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products.
Capsules shell made of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose:
-Capsules shell made of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose contain less residual moisture than gelatin capsules and thus may have applications in filling hydrolytic drugs.
-Also, these capsules alternative for strict vegetarians.
Gelatin
The gelatin used in the manufacture of capsules is obtained from collagenous material (animal connective tissue, bone, skin) by hydrolysis/hydrolytic extraction.
Type of gelatin
There are two types of gelatin, Type A & Type B
| Type A | Type B |
|---|---|
| It is derived mainly from pork skins by acid processing. | It is obtained from bones (“green” (fresh))and animal skins by alkaline processing. |
| Exhibits an isoelectric point in the region of pH 9, | its isoelectric zone in the region of pH 4.7. |
| It contributes plasticity & clarity | Type B (bone) Gelatin contributes firmness |
Note: Blends of both types gelatin are used to obtain gelatin solutions with the viscosity and bloom strength characteristics desirable for capsule manufacture.
Properties of Gelatin
Its physical and chemical properties are mainly functions of the parent collagen, method of extraction, pH value, thermal degradation, and electrolyte content.
- It is a protein in nature so Protein is digested by proteolytic enzyme in GIT hence Gelatin is therapeutically inert.
- It is insoluble in cold water
- Gelatin is soluble in hot water.
- Chemical & physical properties of Gelatin depends upon source of collagen & manner of extraction.
- Taste- tasteless
Physiochemical property of Gelatin
Bloom or gel strength
- Bloom strength measure of the cohesive strength of the crosslinking that occurs between gelatin molecules (i.e. Indicate Cohesive strength of cross-linking-gel strength.
- Bloom strength ∝ to the molecular weight
- Indication of firmness of gel (gel strength)
- Bloom strength –suitable for cap – 150-280g
- It is measured in a Bloom gelometer which determine the weight in grams required to depress a standard plunger (0.5 inches in diameter) to fixed distance/deep (4mm) into the surface of a 6⅔ % w/w gelatin gel under standard conditions. [held at 10°C for 17 hours]
- cost of gelatin is directly proportional to its Bloom or gel strength
Viscosity
- It is a measure of the molecular chain length (i.e. Indicate length of molecular chain)
- Viscosity controls the thickness of cast Film of shell
- 30-60 millipoise is suitable for capsule
- It is measured by Capillary pipette using 6.67 % w/w gelatin gel solution maintained at 60 °C.
Advantage of Capsule
- Better bioavailability – Gelatin shall rapidly dissolves & ruptures.
- Required minimum amount of excipient & little pressure (economic)
- Capsule are easily swallowed as capsule become slippery with moisture in buccal cavity.
- Two incompatible drug can be administered by modifying one drug in tablet or micro encapsulation.
- Drug having unpleasant odour & taste can be administered by enclosing them in a tasteless capsule shell.
- Capsules are made from gelatin; hence they are therapeutically inert.
Disadvantages of Capsule
- Not used for extremely soluble drug KBr, KCl, NH4Cl, Sudden rapid release of drug – High Conc. at localized area -cause gastric irritation.
- Capsule could not used for high Deliquescent or efflorescent or hygroscopic materials.
- Deliquescent – capture Moisture – Cap shell become dry – brittle
- Efflorescent – lose moisture in surrounding – shell become soft
- They cannot be used for substances that react with or dissolve gelatin, the major component.
- Capsule can be easily tempered.
In general, it is recommended that patient should remain 90 sec or more after taking tablets or capsules & that they should be swallowed with at least 100ml of water.
Type of Capsule
Depending on the nature of the capsule shell., Capsules may be classified mainly as either hard or soft. Other types of capsules are Modified release & Enteric Capsules.
- Hard Gelatin Capsule
- Soft Gelatin Capsule
- Modified Release Capsule
- Enteric Capsule

Hard Gelatin Capsule
Hard gelatin capsule is composed of two pieces (cap & body) in the form of cylinders closed at one end; the shorter piece called the ‘cap’ and the longer piece, called the ‘body,. Cap cover body part of capsule & body holds drug substance.
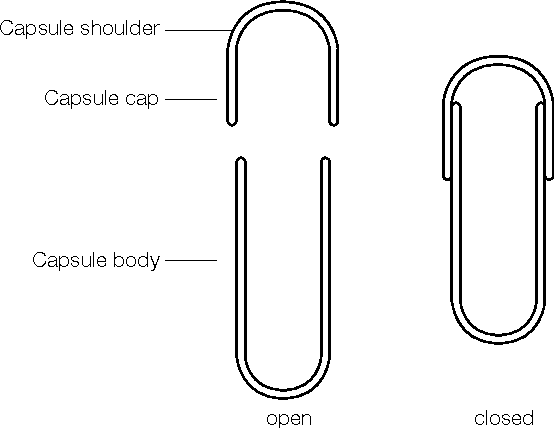
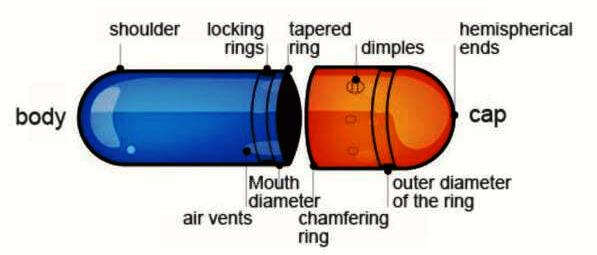
Manufacturing of Hard Gelatin Capsule
Hard gelatin capsule are manufactured in one operation & filled in a completely separate operation.
I. Shell composition of Hard Gelatin Capsule-
- Gelatin – often used a combination of pork skin & bone gelatin
- Colorant- Dye, pigments (Iron oxides)- commonly used (Iron < 15ppm)
- Opaquing Agents – TiO2 (titanium dioxide)- use to render shell opaque & to provide protection against light or to conceal the contents of the capsule
- Preservatives methyl & propylparaben
- USP –SO2 – prevent decomposition during manufacturing
- Water – Purified water Deionised water used to prepare gelatin solution for the preparation of dipping solution.
- Plasticizers: Sorbitol & Glycerol
II. Shell manufacturing
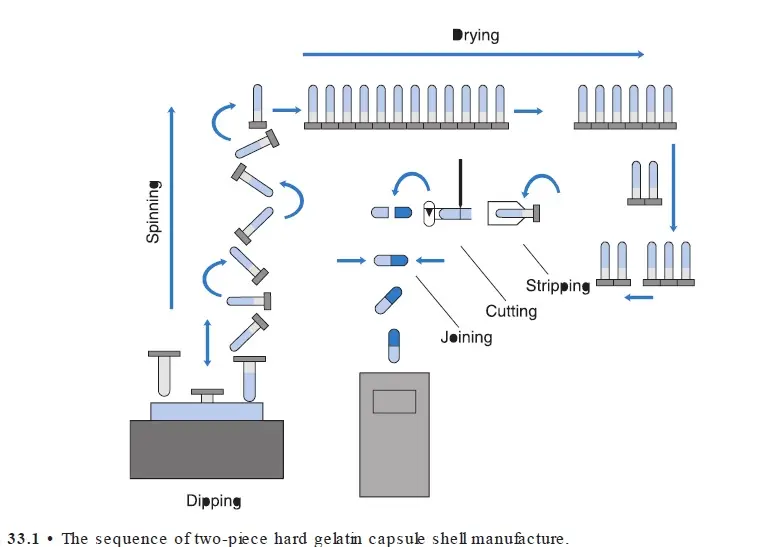
- Dipping – Dipping into gelatin solution @ 50°C – Pin (made of stainless steel) @ 22 °C; Dipping time about – 12 sec
- Rotation/ spinning – helps to distribute the gelatin over pins uniformly.
- Drying – dry air over the pins
- Stripping – use bronze jaws to strip the cap & body from pins
- Trimming – Knives – trim them to the required length – collects & hold cap & body
- Joining – Two portion cap & body are slowly pushed together
III. Shorting –
- Adjustment of moisture content
- Removal of defective capsules
(IV). Printing /Imprinting – Printed prior to filling (on Empty capsules)
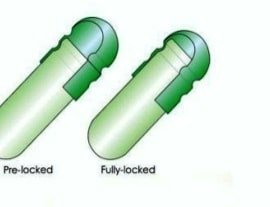
(V) Sealing & Self Locking:-
- Self locking – by forming groves on the inside of the cap & body portion.
- Hermetically Sealed – film of gelatin is laid down around the seam of cap & body.
- Spot welding – two hot metal jaws are through into contact with the area where the cap overlaps the filled body [locking cap body]
(VI) Storage & stability considerations of hard gelatin capsule:-
- Moisture can diffuse through the gelatin wall/film
- Finished Hard gelatin capsules storage condition – optimum 13-16% moisture content-USP, (12-15% Lackman books)
- moisture content < 12% – shell become– brittle
- if moisture content >18% – shell become too soft
- So storage condition 40-60% relative humidity & Temperature 100 °Fahrenheit
- Insolubilization of gelatin /Low water solubility of Gelatin problem
- Due to presence of Aldehyde & High humidity & temp, result into cross-linking of tanning of gelatin which result in failure to the dissolution of capsule shell in GIT.
- To prevent cross-linking of gelatin, Fumaric acid (up to 1%) used to reduce aldehyde tanning of gelatin capsule shell.
- Empty Capsule size variation as a result of moisture content variation
Size of Capsule
| Size of capsule for human use | Volume (mL) | m=V d (in gm) |
| 000 | 1.37 | |
| 00 | 0.95 | |
| 0 | 0.68 | |
| 1 | 0.50 | |
| 2 | 0.37 | |
| 3 | 0.30 | |
| 4 | 0.21 | |
| 5 | 0.13 |
The approximate capacity for capsules from 000 to 5 ranges from 600 to 30 mg, depending on the densities of the powdered drug materials
For Animals use, Size of Capsule:
Size Capacities
10 – 30 gm
11 – 15 gm
12 – 7.5 gm
Selection of size of capsule
Capsule fill weight = tapped Bulk density of formulation x Capsule body volume or
Capsule fill weight= = specific gravity of the liquid x Capsule body volume x 0.8
- Selection of size of capsule –
Capsule fill wt. = tapped Bulk density of formulation Cap body volume
= specific gravity of the liquid Cap body volume 0.8
Type of Material for filling into Hard Gelatin Capsules
- Dry solid –
- Powder
- Pellets
- Granules
- Tablets
- Semisolid –
- Pastes
- Thermosetting mixture
- Thixotropic mixture
- Liquids – Non-aqueous liquid
Note: Material (to be encapsulated) must not react with Gelatin shell.
The basic step in powder filling in the hard gelatin capsule
- Loading of empty capsule shell in filling machine
- Rectification of the capsule shell
- Separation of the body & cap.
- Filling the body with the formulation
- Joining of the body & cap
- Ejection of the filled capsule
- Finishing – Dusting & Polishing –
- Pan polishing
- Cloth dusting
- Brushing
Soft Gelatin Capsule
The soft gelatin capsule was invented by Mothes, a French pharmacist, in 1833. It is One piece, hermatically sealed of gelatin shell containing, liquid, a suspension or a semisolid.
Soft gelatin capsules also referred to as soft shell capsule, soft elastic capsule, or softgel are single-unit solid dosage form, consisting of a liquid, semi-solid, dry powders, or even preformed tablets fill enveloped by a one-piece hermetically sealed elastic outer shell.
Soft gelatin capsules are available in a wide variety of shapes (e.g. round, oblong, tubular). The gelatin is plasticized by the addition of glycerin, sorbitol, or other suitable material, which gives the shell its characteristic flexibility.
Soft gelatin capsules are generally filled with liquids, where the drug is dissolved or dispersed in a solvent.
Capsule Shell Water Content:
Shell water content in Soft Gelatin Capsule – 6 to 10% (hard gelatin capsule water shell content 13 to 16%): USP
Composition of Soft Gelatin Capsule Shell
- Gelatin – Cost of gelatin depends uponits bloom/gel strength. Both type A & B mixture is used.
- Plasticizer- sorbitol or glycerol – uses to make the soft gel elastic
- Preservative – methylparaben & propylparaben – 0.2%
- Coloring & pacifying – TiO2 up to 0.2 to 1.2% & unsoluble dye & pigment
- Flavouring – ethyl vanillin -0.1% / Sugars –Sucrose – 5% – Chewable capsule
- Iron – upto 15 ppm in gelatin
- Fumaric acid – 1% – to reduce aldehyde tanning of gelatin.
Shell Hardness Ratios & their uses (Soft Gelatin Capsule)
- Hardness Ratio= Ratio by wt. of dry plasticizer to dry gelatin.
- As the quantity of plasticizer increases, the Softness of the capsule also increases.
| Capsule | Ratio | Use |
| Hard | 0.4/1 | Oral oil based or shell softening products & for hot, humid areas |
| Medium | 0.6/1 | Vaginal oil base water miscible, oral, tube or shell hardening products & temperate areas |
| Soft | 0.8/1 | Tube, Vaginal, water miscible or shell hardening products & for cold, dry areas |
Note– Volatile liquid cannot be included in the capsule. Since they can migrate into the hydrophilic gelatin shell & volatilize from its surface.
Capsule dosage form
Manufacturing of Soft Gelatin Capsule
The capsule shells of soft capsule are made and filled simultaneously operation while Hard gelatin capsule are manufactured in one operation & filled in a completely separate operation.
- Plate Process read more…
- Rotary-Die Process read more…
- Norton Capsule Machine read more…
- Accogel Capsule Machine (Used to fill dry powder into a soft gelatin capsule) read more…
- Seamless Process (Bubble Method) read more…
- Microencapsulation read more…
Note: Click here for Manufacturing of Soft gelatin capsule in Detail
Environment condition for Soft Gelatin Capsule manufacturing
- Operating area – Temperature. – 20 – 22 °C
- humidity upto 40%
- Drying area =20% to 30% humidity
- Manufacturing of capsule shell & filling of medicament takes place simultaneously.
Evaluation of Capsule
- Content of active ingredients
- Uniformity of contents
- Uniformity of weight
- Disintegrations
- Dissolution
| 1. Content of Active ingredients | 2. Uniformity of contents | 3. Uniformity of weight |
| -Assay- calculate the amount of active ingredients of each capsule. – Take 20 capsules [not less than 5] -Limit = 90-110% | -This test is applicable to capsules that contain less than 10mg or 10% w/w of active ingredients -Active ingredient >10% w/w carry out the test for each ingredient. -This test should be carried out only after the content of active ingredients is passed. – take 10 Capsules, random & Determine active content. None of the capsules: outside range of 75%-125% & Not more than one -85%-115% . -If 2 or 3 cap- outside 85%-115% of avg. value, Repeat test using Another 20 capsules = total 30 capsules, Not more than 3 capsules outside the limit 85%-115% & none is outside the limit 75% -125% in total 30 cap. -omply/ pass test -This test is not applicable for cap. Containing multi-vitamins & trace elements | Not applicable to capsule that are required to comply with the test for “Uniformity Content” Capsule to be taken -20 Weight each intake capsule then open the capsule without losing any part of the shell & remove the whole field content as completely as possible and weight. the shell. Differences in weight is the “weight of contents”. Determine the Average weight. Not more than two of individual weight deviate from the avg. wt. by more than the % shown in below table –Avg. wt. of cap. contents-Less than 300 mg-10% deviation allowed. –Avg. wt. of cap. contents-300 mg or more than 300 mg-7.5% deviation allowed. |
4. Disintegration test
- Temperature: 37±2%
- Disintegration time for Hard gelatin capsule – 30 minutes
- Disintegration time for Soft gelatin capsules – 60 minutes
- Enteric coated capsules – 2hrs – 0.1m HCl then (60 min – phosphate buffer PH 6.8)
- Modified release capsule, The disintegration test is NOT Applicable.
Note- For hard & soft gelatin capsule for which the dissolution test is included in the monograph, the test for disintegration is not required [Not applicable for the capsule which requires dissolution test ]
Disintegration test
5. Dissolution
The rate and extent of dissolution of the drug from the capsule dosage form is tested by a dissolution test.
The dissolution test for capsules uses the same apparatus, dissolution medium, and test as that for uncoated and plain coated tablets.
Important key points
- Capsules are not suitable for
- Substance unstable in the presence of moisture. Eg. Aspirin
- Water-soluble liquid & volatile cannot be included as major constituents of the capsule content.
- Preparation to be encapsulated-
- pH – 2.5 to 7.5
- More acidic preparation – cause hydrolysis – Result in leakage
- More alkaline – tannin – water solubility of the shell is decreased
- The moisture content of capsule shell determined by – Toluene distillation method










